New Publication: Numerical Simulation of Snowdrift Development in Non-Equilibrium Flow Fields Around Buildings
 Written by rbfLAB on
Written by rbfLAB on
We are pleased to announce the publication of a new collaborative research study conducted by the University of Rome Tor Vergata in partnership with Ansys Japan, titled:
“Numerical Simulation of Snowdrift Development in Non-Equilibrium Flow Fields Around Buildings”
Authors: Ryu Nara, Corrado Groth, and Marco Evangelos Biancolini.
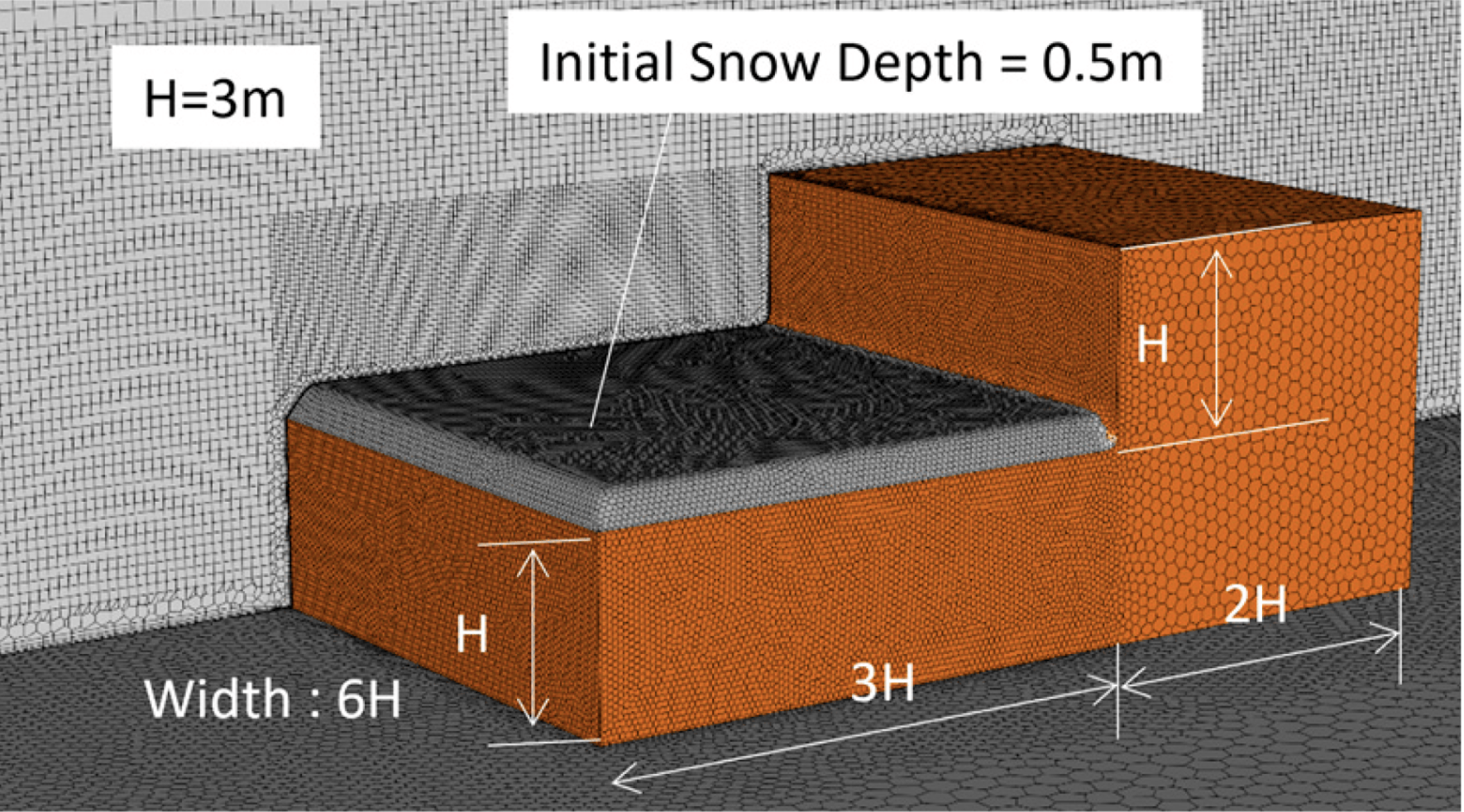
This study presents a numerical approach to analyzing transient snow drifting phenomena around buildings. Using the commercial CFD software Ansys Fluent, enhanced with user-defined functions (UDFs) to account for snow transport, the research explores snow accumulation under non-equilibrium flow conditions—an area where validation data has been limited.
Snowdrift development was simulated for three types of flow environments, incorporating the concept of saltation fetch distance to model snow transport rates more accurately. Simulation results were compared with actual field measurements to assess the model’s predictive performance.
Key findings include:
- Cube-shaped buildings and two-level flat roofs exhibited strong agreement between simulations and measured snowdrift patterns.
- In contrast, simulations of snow fences resulted in a noticeable underestimation of snow accumulation downstream, indicating areas for further refinement.
This work contributes to the ongoing advancement of computational snowdrift modeling, offering valuable insights for infrastructure design and resilience planning in snow-affected regions.
For further information or to access the full study: https://www.mdpi.com/2311-5521/10/4/75#


Comments